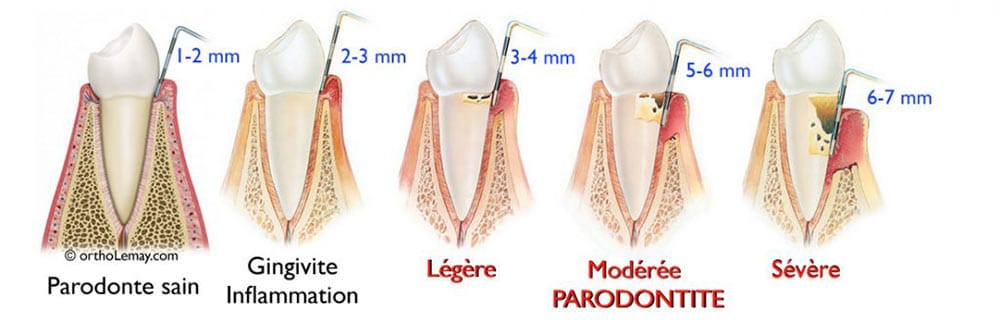
Periodontium refers to the tissues that support the teeth: gingiva, alveolar bone, the ligament that allows the tooth to move slightly within the bone, and cementum, which acts as a glue between the ligament and the tooth. Periodontal disease therefore encompasses diseases that affect these tissues: gingivitis and periodontitis.
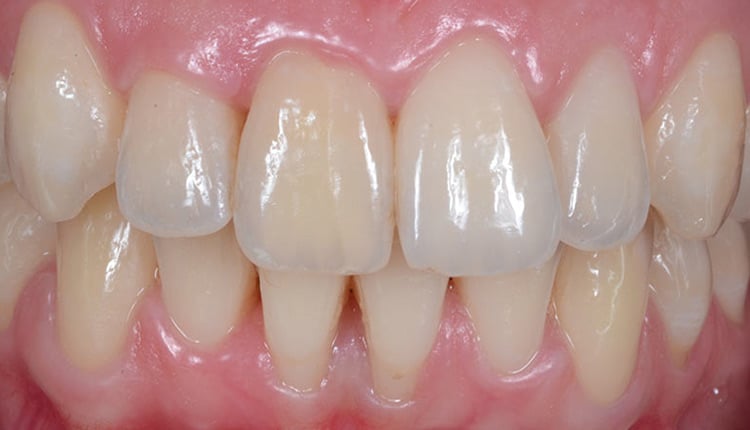
Gingivitis is a bacterial inflammation of the gums that causes swelling, redness and bleeding. Its effects are reversible after appropriate treatment.
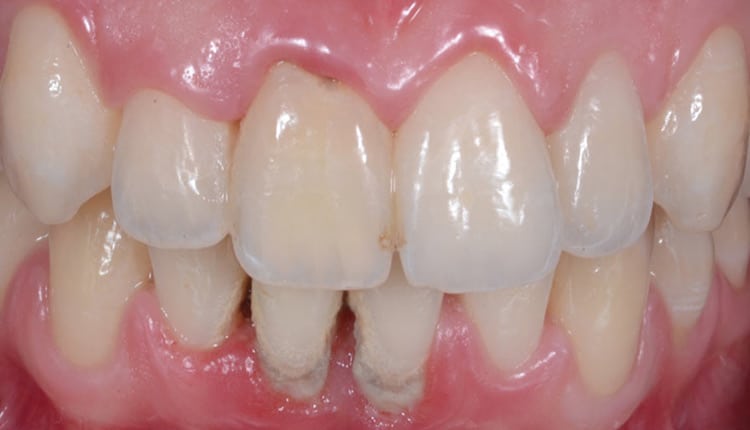
Periodontitis, on the other hand, is gingivitis that has progressively worsened, attacking not only the gums, but also the bone supporting the teeth. It leads to loosening of the teeth: the roots of the teeth are exposed. If the progression of the disease is not stopped in time, it can lead to the loss of the affected teeth.
A periodontist is a dentist who specializes in the treatment of these diseases. That’s why it’s important to go to a periodontist rather than a non-specialized dentist.